
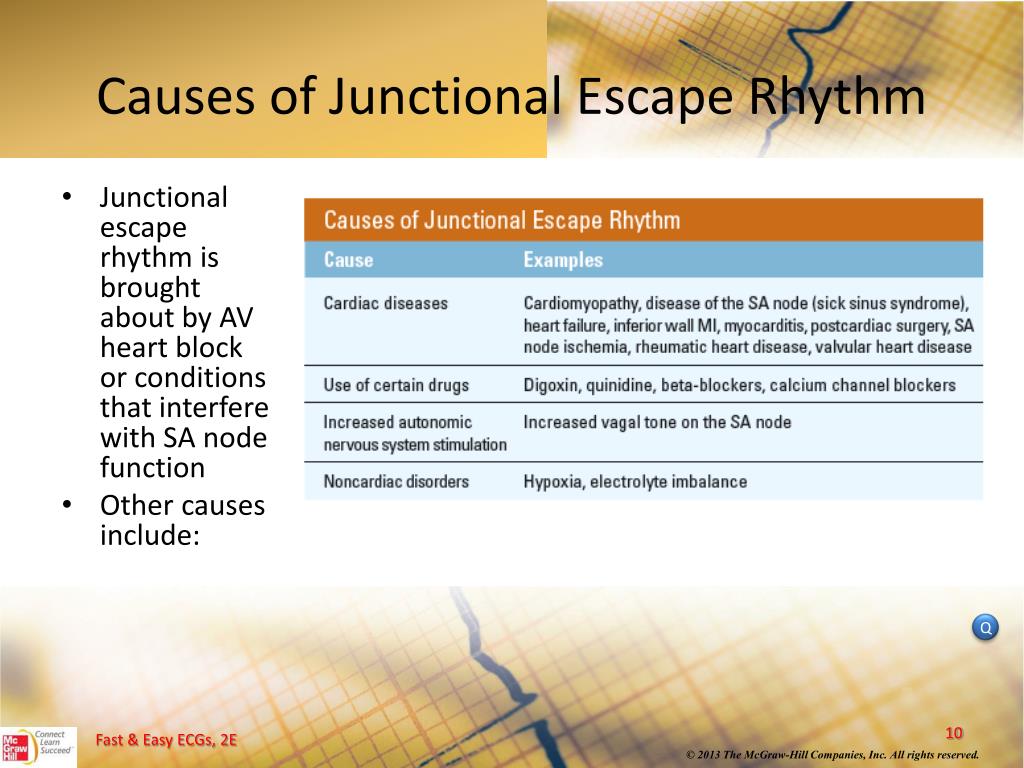
In patients with complete AV block, high-grade AV block, or symptomatic sick sinus syndrome (ie, sinus node dysfunction), a permanent pacemaker may be needed. No pharmacologic therapy is needed for asymptomatic, otherwise healthy individuals with junctional rhythms that result from increased vagal tone. Read More: What are the 3 levels of the ecological model? What is the treatment for junctional rhythm? If it is upside down in any other lead, then the likely causes are ischaemia or ventricular hypertrophy (Fig.

QRS complexes are typically narrow ( 100 bpm.Junctional rhythm with a rate of 40-60 bpm.2008 Jul-Aug 36(4):691-8.What are the characteristics of a junctional rhythm? Anatomical aspects of the arterial blood supply to the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes of the human heart. Pejković B, Krajnc I, Anderhuber F, Kosutić D. Arterial blood supply of the atrioventricular node and main bundle. Van der Hauwaert LG, Stroobandt R, Verhaeghe L. Structure, function and clinical relevance of the cardiac conduction system, including the atrioventricular ring and outflow tract tissues. 1977 Jun 93(6):735-40.ĭobrzynski H, Anderson RH, Atkinson A, Borbas Z, D'Souza A, Fraser JF, Inada S, Logantha SJ, Monfredi O, Morris GM, Moorman AF, Nikolaidou T, Schneider H, Szuts V, Temple IP, Yanni J, Boyett MR. Correlations with electrocardiographic findings in 111 patients. Thery C, Gosselin B, Lekieffre J, Warembourg H. Normal sinus heart rate: sinus tachycardia and sinus bradycardia redefined. Junctional tachycardia: rate above 100 beats per minuteĬopyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC. Junction escape rhythm: rate 40 to 60 beats per minuteĪccelerated junctional rhythm: rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute

Junctional bradycardia: rate below 40 beats per minute The terminology used to identify the type junctional rhythm depends on its rate and is as follows: This electrical activity then travels through the atria to the AV node from where it reaches the Bundle of His from where the electrical signals travel to the ventricles through the Purkinje fibers. Generally, in sinus rhythm, a heartbeat is originated at the SA node. A junctional rhythm is where the heartbeat originates from the AV node or His bundle, which lies within the tissue at the junction of the atria and the ventricle. The first septal perforator of the left anterior descending artery also supplies blood to the AV node. The blood supply to the AV node is from the AV nodal branch of the right coronary artery (90%) or the left circumflex artery (10%) depending on the right or left dominant blood supply to the heart. The sinoatrial nodal artery supplies blood to the sinoatrial node, it branches off the right coronary artery in 60% of cases, whereas in 40% of cases, it comes from the left circumflex coronary artery.

This anatomic region is also commonly referred to as the triangle of Koch. It sits within an anatomic region bordered posteriorly by the coronary sinus ostium, superiorly by the tendon of Todaro, and anteriorly by the septal tricuspid valve annulus. The atrioventricular node (AV) is a subendocardial structure situated in the inferior-posterior right atrium. The sinoatrial node (SA) is the default pacemaker and is located subepicardially and is crescent in shape.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
